The Supercloud Platform
for API-first applications
Unprecedented cloud distribution, performance and availability at the lowest cost possible
Deliver apps within milliseconds of end users


CloudFlow is your unfair, competitive advantage to deliver world-class digital experiences
Unprecedented Workload Automation
Leveraging AI and ML data, our autonomous location orchestration dynamically optimizes the delivery network for peak efficiency and performance. 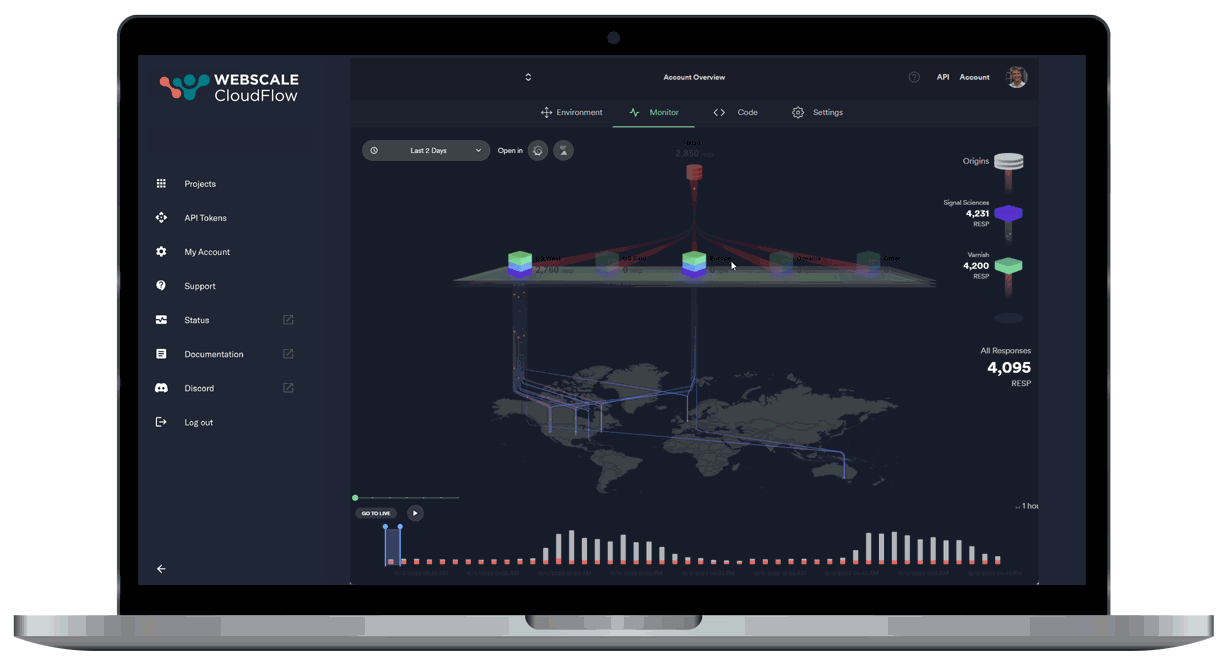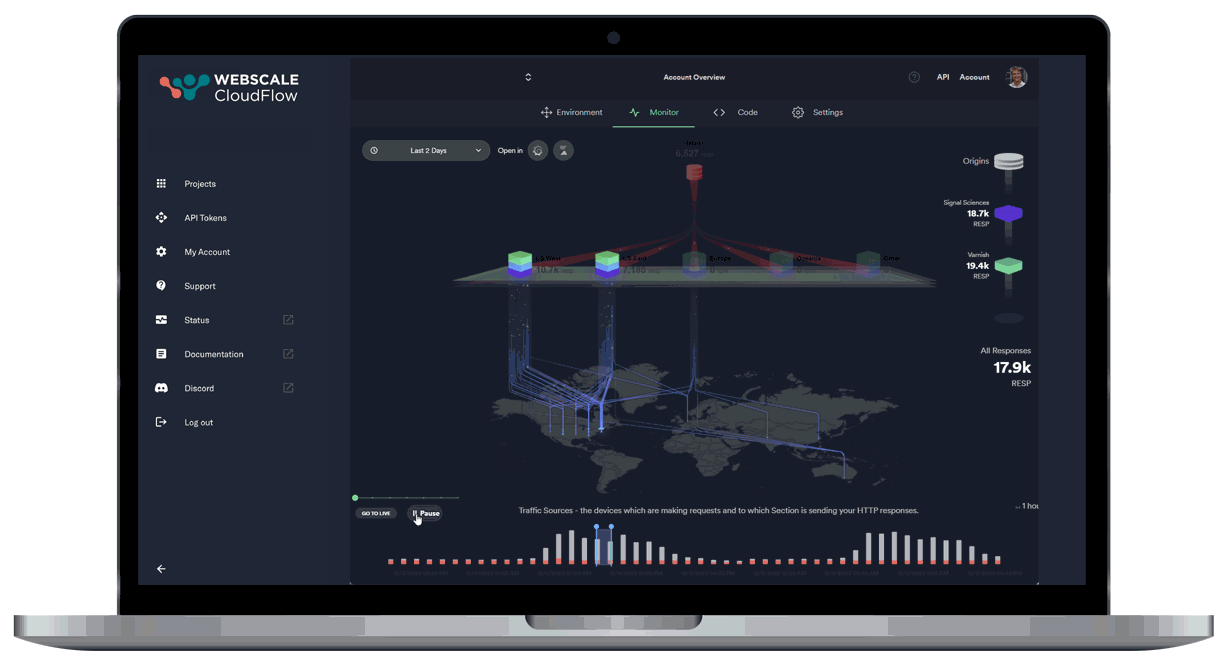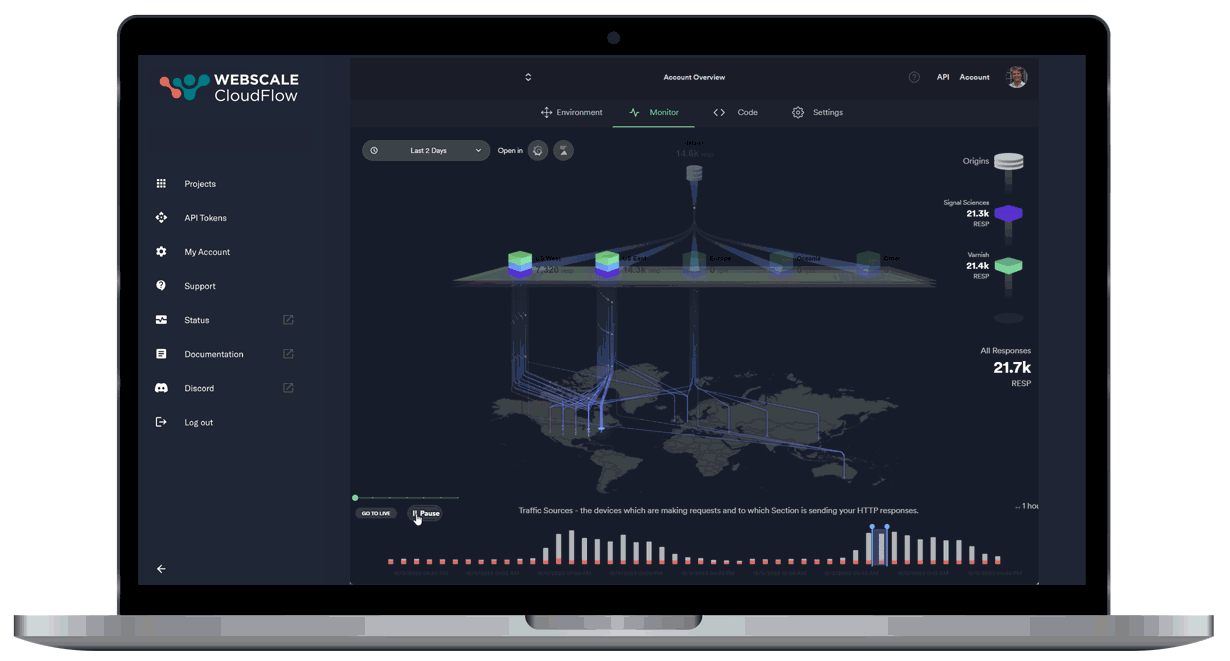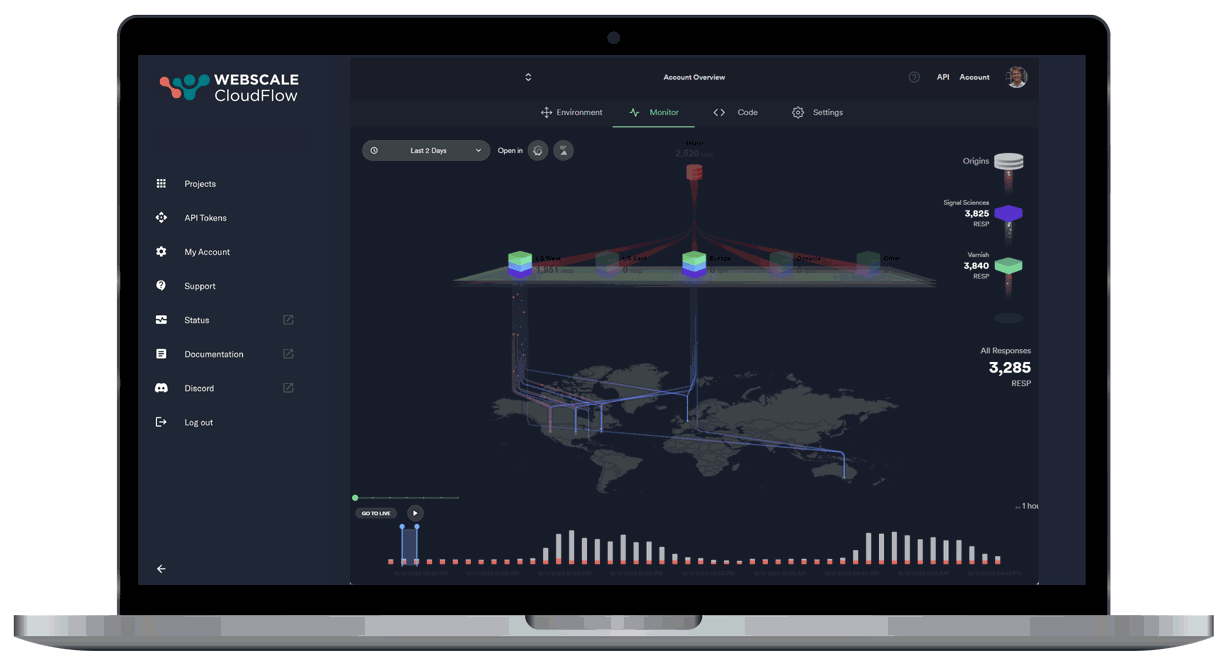
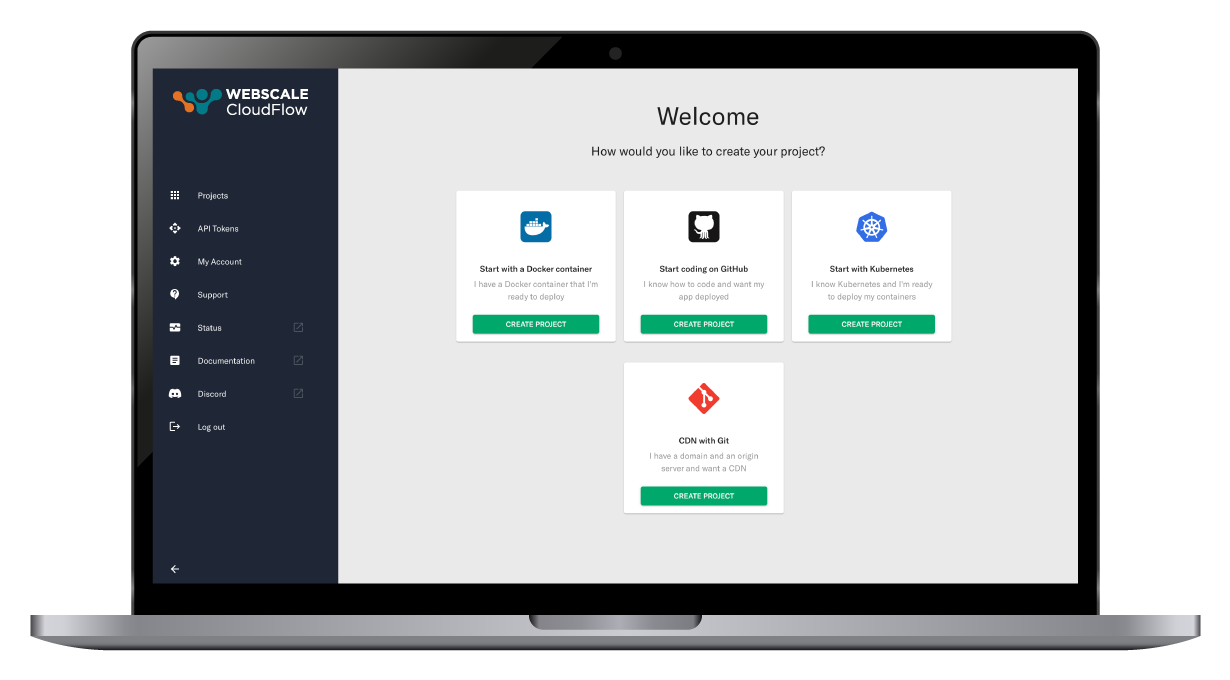
Developer-centric project launch journey
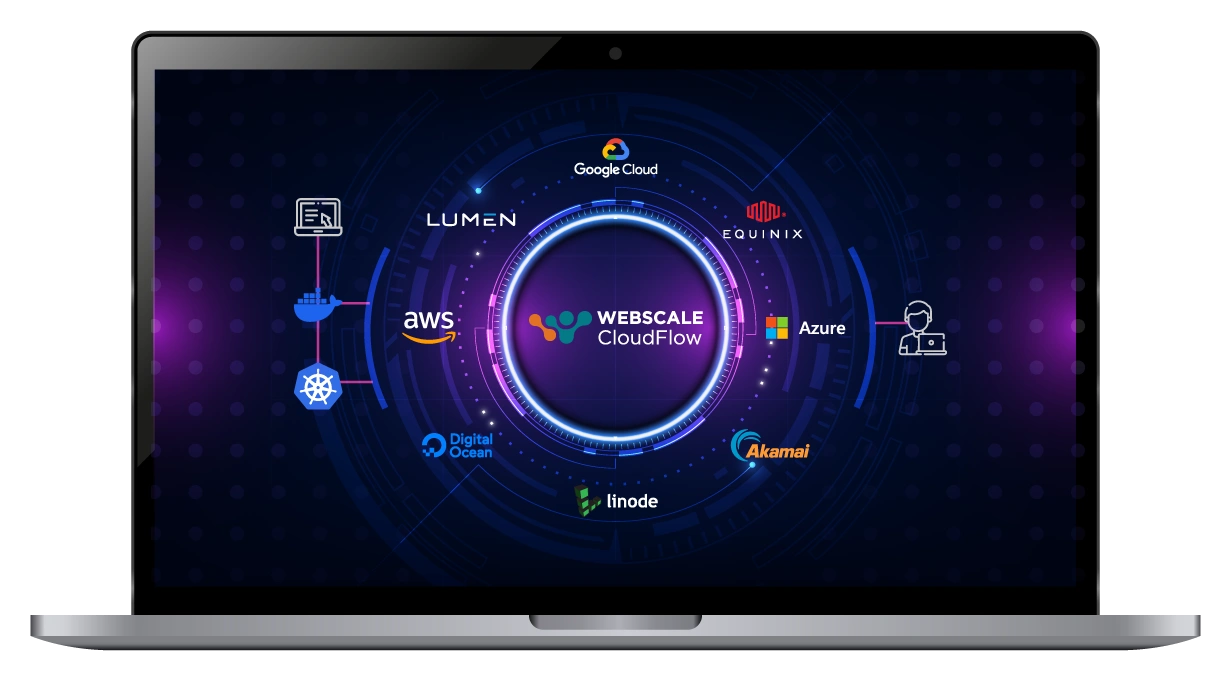
Supercloud distribution at your fingertips
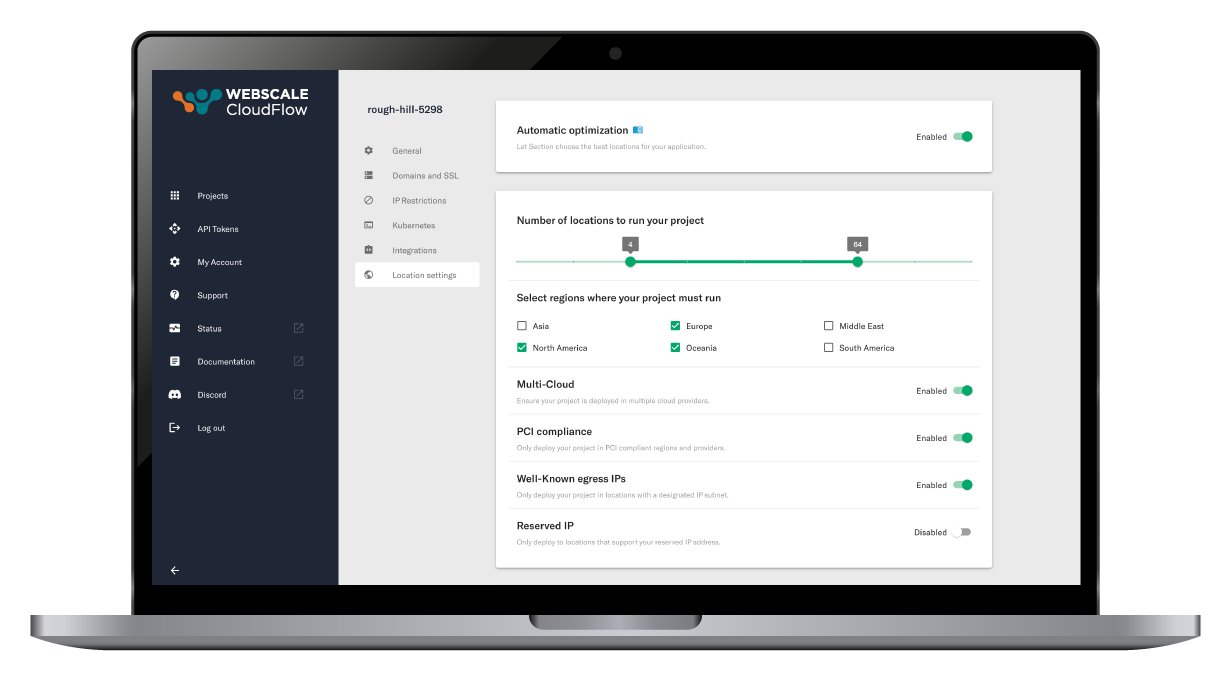
Customize your location policies and guard rails
Unprecedented Workload Automation
Leveraging AI and ML data, our autonomous location orchestration dynamically optimizes the delivery network for peak efficiency and performance.
Developer-centric project launch journey
Effortlessly kickstart your work using a container image, Kubernetes cluster, or directly from a GitHub Repository. Designed for ease and efficiency, our platform simplifies your development journey right from the start.
Supercloud distribution at your fingertips
Experience a truly integrated mesh network, connecting premier public and private cloud providers. This powerful fusion offers your applications a seamless and straightforward gateway to advanced Supercloud computing capabilities.
Customize your location policies and guard rails
Refine your parameters for optimizing the number of locations, preferred regions, compliance requirements, and more. Your policies influence dynamic server locations based on real-time traffic data, minimizing the distance for user requests and adapting to changing traffic patterns.




Supercloud
Simplicity-as-a-Service
The CloudFlow platform automates the orchestration of custom workloads, apps and APIs across a mesh network of private and public cloud providers.
We have created CloudFlow so you can harness the power of distributed, multicloud computing without the operational chaos that is traditionally involved with managing such a complex infrastructure network.


Our study revealed that CloudFlow enhances application performance, reduces cloud cost and eliminates K8s operational complexity
Customer Testimonials
Read our Latest Blogs
How to Solve GraphQL Latency Challenges by Deploying Closer to Your Users
GraphQL is a widely adopted alternative to REST APIs because of the many benefits that it offers, including performance, efficiency, and predictability. While the advantages are significant, many developers become frustrated with latency challenges when implementing...
Headless Commerce Drives Edge Computing Adoption
In e-commerce today, the challenge to meet and exceed customer expectations is driving innovation. The demand for frictionless shopping, 24/7 availability, superior product and impeccable service quality is ever increasing, putting pressure on retailers to deliver...
Two Aspects of Edge Compute to Focus on for Reducing Edge Complexity
As organizations look to capitalize on the benefits of edge computing, many are quickly realizing the complexities associated with building and operating distributed systems – including sourcing distributed compute, resource management/placement/sizing/scaling,...















